TubeTK/Data: Difference between revisions
Roland.kwitt (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* [[TubeTK/Installation|Installation]] | * [[TubeTK/Installation|Installation]] | ||
* [[TubeTK/Documentation|Methods & Apps]] | * [[TubeTK/Documentation|Methods & Apps]] | ||
* [[TubeTK/Slicer|TubeTK with Slicer | * [[TubeTK/Slicer|TubeTK with 3D Slicer]] | ||
* [[TubeTK/OsiriX|TubeTK with OsiriX]] | * [[TubeTK/OsiriX|TubeTK with OsiriX]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 33: | Line 32: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
'''[[TubeTK/ | '''[[TubeTK/Contact|Contact Us]]''' | ||
| width="800px" align="left" | | | width="800px" align="left" | | ||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
=== 100 Healthy Normal MRIs and MRAs from UNC === | === 100 Healthy Normal MRIs and MRAs from UNC === | ||
{|width="100%" | {|width="100%" | ||
|[[File:Intracranial-Teaser.jpg| | |[[File:Intracranial-Teaser.jpg|300px|link=https://data.kitware.com/#collection/591086ee8d777f16d01e0724/folder/58a372e38d777f0721a64dc6]] | ||
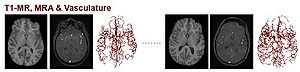
|This dataset contains 100 (T1, MRA) image pairs from healthy patients, acquired by a Siemens Allegra head-only 3T MR system. The voxel spacing for the MRA images is (0.5x0.5x0.8mm) with a volume size of (448x448x128voxel); The voxel spacing for the T1 images is 1mm isotropic with a volume size of (176x256x176voxel). | |This dataset contains 100 (T1, MRA) image pairs from healthy patients, acquired by a Siemens Allegra head-only 3T MR system. The voxel spacing for the MRA images is (0.5x0.5x0.8mm) with a volume size of (448x448x128voxel); The voxel spacing for the T1 images is 1mm isotropic with a volume size of (176x256x176voxel). | ||
The full dataset can be downloaded [ | The full dataset can be downloaded [https://data.kitware.com/#collection/591086ee8d777f16d01e0724/folder/58a372e38d777f0721a64dc6 here]. A subset of this dataset also includes intra-cranial vasculature (centerline + radius), extracted from the MRA images. These models are found in each patient's "Auxillary Data" folder, such as [https://data.kitware.com/#collection/591086ee8d777f16d01e0724/folder/58a372fa8d777f0721a64dfb here]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 54: | Line 53: | ||
{|width="100%" | {|width="100%" | ||
|[[File:REUS-Teaser.jpg| | |[[File:REUS-Teaser.jpg|300px|link=http://midas3.kitware.com/midas/folder/10255]] | ||
|This dataset contains Ultrasound videos, acquired on a (hand-made) noodle phantom. The database is split into template videos and search path videos and is designed to evaluate recognition algorithms. It can be downloaded from [http://midas3.kitware.com/midas/folder/10255 here]. | |This dataset contains Ultrasound (US) videos, acquired on a (hand-made) noodle phantom. The database is split into template videos and search path videos and is designed to evaluate recognition algorithms. It can be downloaded from [http://midas3.kitware.com/midas/folder/10255 here]. | ||
In | In summary (see included README file for details), the database contains videos from 9 different ''noodle'' structures. We provide 10 templates videos per structure (i.e., 90 templates in total) and 9 ''search path'' videos (i.e., 1 search path video per structure). One task could be, for instance, to localize (temporally) the templates in the corresponding search path videos. Currently, the videos are available in (64x64pixel) and (128x128pixel) spatial resolution. | ||
To evaluate recognition algorithms, we further provide human ground truth locations for the search paths, indicating when a structure moves "in" and "out" of the US imaging plane (These annotations were averaged over 5 different persons). | |||
|} | |} | ||
---- | ---- | ||
=== TubeTK Testing | === TubeTK Testing Data === | ||
Another good resource to download data material for experimenting with TubeTK is our testing data, available from [http://midas3.kitware.com/midas/community/7 here]. | Another good resource to download data material for experimenting with TubeTK is our testing data, available from [http://midas3.kitware.com/midas/community/7 here]. | ||
| Line 72: | Line 73: | ||
= Journal Articles = | = Journal Articles = | ||
* R. Kwitt, N. Vasconcelos, S. Razzaque and S.R. Aylard: '''Localizing Target Structures in Ultrasound Video - A Phantom Study''', Medical Image Analysis, vol. 17, no 7., pp. 7127-22, 2013 [http://www.medicalimageanalysisjournal.com/article/S1361-8415(13)00069-8/abstract Publisher Link] [http://public.kitware.com/Wiki/images/3/33/Kwitt13aMedIA.pdf Preprint] | |||
* R. C. Gessner, S. R. Aylward, and P. A. Dayton: '''Mapping Microvasculature with Acoustic Angiography Yields Quantifiable Differences between Healthy and Tumor-bearing Tissue Volumes in a Rodent Model''', Radiology, vol. 264, no. 3, pp. 733–740, 2012. | * R. C. Gessner, S. R. Aylward, and P. A. Dayton: '''Mapping Microvasculature with Acoustic Angiography Yields Quantifiable Differences between Healthy and Tumor-bearing Tissue Volumes in a Rodent Model''', Radiology, vol. 264, no. 3, pp. 733–740, 2012. | ||
* E. Bullitt, D. Zeng, B. Mortamet, A. Ghosh, S. Aylward, W. Lin, B. L. Marks, and K. Smith: '''The effects of healthy aging on intracerebral blood vessels visualized by magnetic resonance angiography'''. Neurobiology of Aging, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 290–300, 2010. | * E. Bullitt, D. Zeng, B. Mortamet, A. Ghosh, S. Aylward, W. Lin, B. L. Marks, and K. Smith: '''The effects of healthy aging on intracerebral blood vessels visualized by magnetic resonance angiography'''. Neurobiology of Aging, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 290–300, 2010. | ||
| Line 96: | Line 98: | ||
= IPMI and MICCAI Publications = | = IPMI and MICCAI Publications = | ||
* R. Kwitt, D. Pace, M. Niethammer and S. Aylward: '''Studying Cerebral Vasculature Using Structure Proximity and Graph Kernels'''. In: MICCAI '13 | * R. Kwitt, D. Pace, M. Niethammer and S. Aylward: '''Studying Cerebral Vasculature Using Structure Proximity and Graph Kernels'''. In: MICCAI '13, vol. 8150, pp. 534-541, 2013 [http://public.kitware.com/Wiki/images/3/3f/SupplementaryMaterial.pdf Supplementary Material] [http://public.kitware.com/Wiki/images/e/e5/Kwitt13bMICCAI.pdf PDF] | ||
* R. Kwitt, N. Vasconcelos, S. Razzaque and S. Aylward: '''Recognition in Ultrasound Videos: Where am'''. In: MICCAI '12, vol. 7512, pp. pp 83-90, 2013 ('''Oral presentation''' ; Acceptance rate < 5%; Winner of the '''MICCAI Young Scientist Award''') [http://public.kitware.com/Wiki/images/a/af/Kwitt12aMICCAI.pdf PDF] | |||
* J. Jomier, E. Bullitt, M. Van Horn, C. Pathak, and S. Aylward: '''3D/2D model-to-image registration applied to TIPS surgery'''. In: MICCAI’06, vol. 4191, pp. 662–669, 2006 | * J. Jomier, E. Bullitt, M. Van Horn, C. Pathak, and S. Aylward: '''3D/2D model-to-image registration applied to TIPS surgery'''. In: MICCAI’06, vol. 4191, pp. 662–669, 2006 | ||
| Line 148: | Line 152: | ||
* S. Aylward, S. Pizer, D. Eberly, and E. Bullitt: '''Intensity Ridge and Widths for Tubular Object Segmentation and Description'''. In: MMBIA ’96 p. 131-138, 1996 | * S. Aylward, S. Pizer, D. Eberly, and E. Bullitt: '''Intensity Ridge and Widths for Tubular Object Segmentation and Description'''. In: MMBIA ’96 p. 131-138, 1996 | ||
[[Category:TubeTK|Data]] | |||
[[Category:TubeTK Data|*]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:01, 31 May 2017
__NOTITLE__
|
|
Data100 Healthy Normal MRIs and MRAs from UNC
Recognition in Ultrasound (REUS) Database
TubeTK Testing DataAnother good resource to download data material for experimenting with TubeTK is our testing data, available from here. Patents
BooksS. Aylward and E. Bullitt, Chapter 11: Clinical Applications Involving Vascular Image Segmentation and Registration. Angiography and Plaque Imaging: Advanced Segmentation Tequniques, Academic Press, 2002 pp. 529-579 Journal Articles
IPMI and MICCAI Publications
Other Conference Papers
|