Animation View
Animation View is used to set up animations in ParaView. It's is accessible through View | Animation View. This article describes this view and how to use it to create simple animations.
User Interface
|
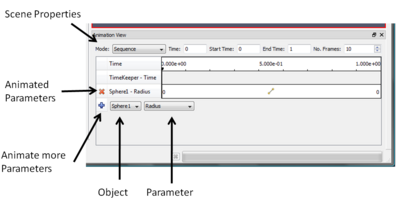
Figure 1 shows the the animation view. It is a standard dockable widget. There are three major portions to this panel:
|
Animate Parameters
|
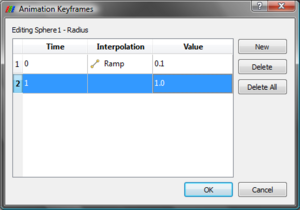
One of the simplest animation set up is where the user wants to change a parameter on a filter or source through the course of the animation. Consider the simplest case, we have a sphere source and we want to create an animation where the radius of the sphere goes from 0.1 to 1. Say the sphere source we want to animate is called "Sphere1" in the pipeline browser. Now to add an animation track to animate the radius of this sphere, select the Sphere1 in the Object combo-box and then select Radius in the Parameter combo-box. Then hit theError creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination to add the animation track for Sphere1's Radius. Once the track is added it will be shown in the Animated Parameters section. Now, we need to change the radius value to go from 0.1 to 1. So, simply double click on the track, the Animation Keyframes editor dialog will pop-up (Figure 2). ParaView tries to initialize new animation tracks with some default values, hence this track has been initialized to animate the raduis from 0 to 0.5. To change any parameter, simply double-click on any column and enter the new values.
ParaView's animation engine is key-frame based. Hence one can add more than two keyframes, change the interpolation function for the value between two keyframes etc. using this dialog. Double-clicking on the Interpolation column will show the available interpolation functions for the given parameter type. Note that there's no interpolation function for the last key-frame since interpolation is defined between two keyframes. To remove an animation track, simply hit theError creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination next to that animation track.
|
Animate Opacity/Visibility
Similar to animating any filter/source paramters, it is possible to animate the opacity or visibility of the object in all the views that it's shown. In the Parameter combo simply choose Opacity or Visibility when adding the animation track.
Time in ParaView
Before we delve any further into the world of animation, we need to understand time as ParaView implements it.
There are three types of times in ParaView:
- Animation Time:
- This is the time that changes as an animation is played.
- The VCR buttons in the toolbar, moving the time cursor on the animation view changes this animation time.
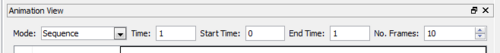
- The time-toolbar (Figure 3) shows the animation time.
- Reader Time:
- Certain file formats support associating time with datasets eg. exodus, XML VTK formats etc. This is referred to as a the reader time.
- The information tab shows the timesteps provided by any reader/data source (Figure 4).
- Note that when multiple sources provide time, ParaView assumes that they are all in the same time units.
- Application (TimeKeeper) Time
- This refers to the application wide time. This is the time value that ParaView requests from the readers/sources for showing data in any of the views.
- By default, this is linked with the animation time i.e. it's same as the animation time. However that can be changed by using the TimeKeeper-Time animation track on the Animation View. Double click on the track to pop-up the key-frames editor dialog which allows for setting this to a constant time value (useful in making animations where the data time should not change) or add explicit keyframes (Figure 5).
Play Modes
ParaView has three animation play-back modes. The mode as well as the parameters for each mode can be set in the scene properties section of Animation View (Figure 1).
- Sequence
- In this mode the animation is played as a sequence of frames evenly spaced in the specified Start Time and End Time for the animation. The No. Frames controls the number of frames in the animation. During playback, the animation time goes from Start Time to End Time incremented by (end time-start time)/(no. of frames) for every consecutive frame.
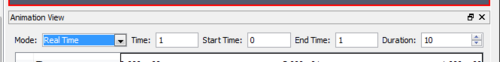
- Real Time
- In this mode the animation is played for the specified Duration in seconds (approx.). The animation time increases from Start Time to End Time. The number of frames actually rendered depends on how long each frame takes to render since the entire animation has to be done within the specified duration.
- Snap To TimeSteps
- This mode is useful when a file with data at different timesteps is opened. When in this mode, the animation time increases from Start Time to End Time producing exactly as many frames at the number of timesteps, with each frame corresponding to a timestep. One can think of this mode as going through the time-steps in a sequence.

Animate Data Timesteps
When a dataset with timesteps is loaded, ParaView detects it, updates the start and end times for the animation scene to match those provided by the reader and then switches the play mode to Snap To TimeSteps. Thus, there's no explicit setup that the user needs to do to cycle through the timesteps; simply hit play and ParaView will run through the time steps.